![]()
PHY385 Module 2
Student Guide
Concepts of this
module
Superposition principle
Electromagnetic wave
Complex form of the wave
function
Energy density and Poynting
vector
Quiz
![]()
Activity 1 - Superposition principle
I. You will
watch the superposition of two disturbances with animations created by Prof.
Daniel Russell from
The two pulses are traveling
1. in the opposite direction; and
2. in the same direction.
What is the amplitude of the resulting disturbance in any location of space in case (1) and case (2)?
Give your estimate of a speed of propagation of the disturbance in the cases (1) and (2)?
The two waves
are traveling
3. in the opposite direction;
4. in the same direction with an observer at rest in the reference frame of one of the wavefronts; and
5. in the same direction with slightly different frequency
Treating the amplitude as the maximum possible magnitude of the disturbance (displacement), what is the amplitude of the resulting wave in the cases (3), (4) and (5)?
What is the wavelength of the resultant in the cases (3) - (5)?
What is the frequency of the resulting disturbance in the cases (3) - (5)?
II. The superposition principle states that the superposition of the waves is also a wave.
1. Determine which of the following describe traveling waves:
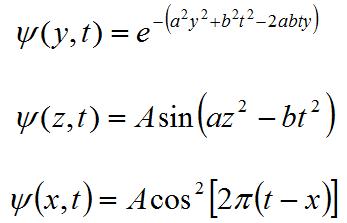
2.
For the traveling wave(s) from the above list, write the direction of
propagation and the speed of the wave.
3. Choose any one of the traveling waves determined
above. Prove that the superposition of the two of such waves is also a wave.
![]()
Activity 2 -
Electromagnetic wave
A 550-nm
harmonic EM wave whose electric field is in the z-direction is traveling in the
y-direction in vacuum.
1. What is the frequency of the wave?
2. Determine ω and k
of the wave.
3. If the electric field amplitude is
600 V/m, what is the amplitude of the magnetic field?
4. Write an expression for E(t)
and B(t) given that each is zero at x
= 0 and t = 0. Put in the appropriate
units
Please
make a table in your notebook to order the following forms of electromagnetic
radiation from shortest to longest wavelength, and, for each, list:
| Column
1: Name | Column 2: Wavelength range | Column 3: Photon energy |
Column 4: Applications, properties or concerns.
Gamma Rays
Infrared Radiation
Microwaves
Radio Waves
Ultraviolet
X-rays
Visible Light
![]()
Activity 3 - Complex
form of the wave function
An electromagnetic wave is specified
(in SI units) by the following equation:
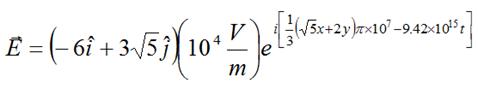
Find
a)
the direction along which the
electric field oscillates;
b)
the scalar value of amplitude of the
electric field;
c)
the direction of propagation of the
wave;
d)
the propagation number of the
wavelength;
e)
the frequency and the angular
frequency; and
f)
the speed of the wave.
![]() Activity 4 - Energy density and
Poynting vector
Activity 4 - Energy density and
Poynting vector
Consider a linearly polarized plane
electromagnetic wave traveling in the + x direction in free space having
as its plane of vibration the xy- plane. Given that its frequency is10
MHz and its amplitude is E0
= 0.08 V/m,
1. Find
the period and wavelength of the wave.
2. Write
an expression for E(t) and B(t).
3. Find
the expression for the Poynting vector S.
4. The
flux density of the wave is the time average of the magnitude of the Poynting
vector S. Find the flux density <S> of the wave.
5. Find
the energy density of the wave.
6. Prove
that the energy densities of the electric and magnetic fields are equal ( uE
=uB ) for electromagnetic field
This Student Guide was written by
Jason B. Harlow, Dept. of Physics,
Last updated by Natalia Krasnopolskaia in September
2014.