PHY405 Electronics, Resources
Adapted from Prof. David Bailey's website in 2022
Course Materials
Books
There is no required textbook for the course, and you should not need to have one, but the following may be useful if you are keen to know more about electronics.
- The Art of Electronics by Paul Horowitz and Winfield Hill, 3rd Ed.
- Basic electronics for scientists by James Brophy
- Basic Electronics for Scientists and Engineers by Dennis L. Eggleston
Free Online Books
Circuit Simulators
For this course, we use this very simple browser based pedagogical circuit simulator:
- the Paul Falstad circuit or filter simulators.
- Engineer Sayanee Basu has a nice Circuit simulation with Falstad introduction, and Iain Sharp has a longer beginner tutorial.
- An alternate port for this simulator can be accessed at lushprojects.com
- Note that the circuit and filter simulators are closely related but different. The circuit simulator allows you to look at voltages, currents, and signals in the circuit. The filter simulator gives attenuation and phase plots for filter circuits with inputs and outputs.
Other more powerful professional circuit simulators exits, but the only one referenced by this course is:
Manuals
- Keysight DSOX1204G Digital Storage Oscilloscope with Function Generator
- Data Sheet
- User Guide, also available directly from Keysight
- Programming Guide, also available directly from Keysight
- Keysight EDU36311A Triple Output Bench Power Supply
- Data Sheet
- User Guide, also available directly from Keysight
- Programming Guide, also available directly from Keysight
- Keysight 34461A 6 1/2 Digit Multimeter Supply
- Data Sheet
- Operating Guide (includes Programming), also available directly from Keysight
Code
Components
Resistors
- Resistor colour code description, chart, or calculator
Axial resistor sizes are not precisely standardized, but here are some typical parameters:
| Power rating (W) | Body length (mm) | Body diameter (mm) |
|---|---|---|
| 1/8 | \(\sim 3\) | \(\sim 1.8\) |
| 1/4 | \(\sim 6.5\) | \(\sim 2.5\) |
| 1/2 | \(\sim 8.5\) | \(\sim 3.2\) |
| 1 | \(\sim 11\) | \(\sim 5\) |
Capacitors
Basic ceramic capacitor codes are in the format “DDM”, where the first two digits are the significant figures, the 3rd is the multiplier, and the units are picofarads, i.e. \({DD \times 10^M}\) gives the capacitance value in pF. For example, a capacitor labelled “223” is \(\mathrm{22\times 10^3\,pF = 22\,nF}\)
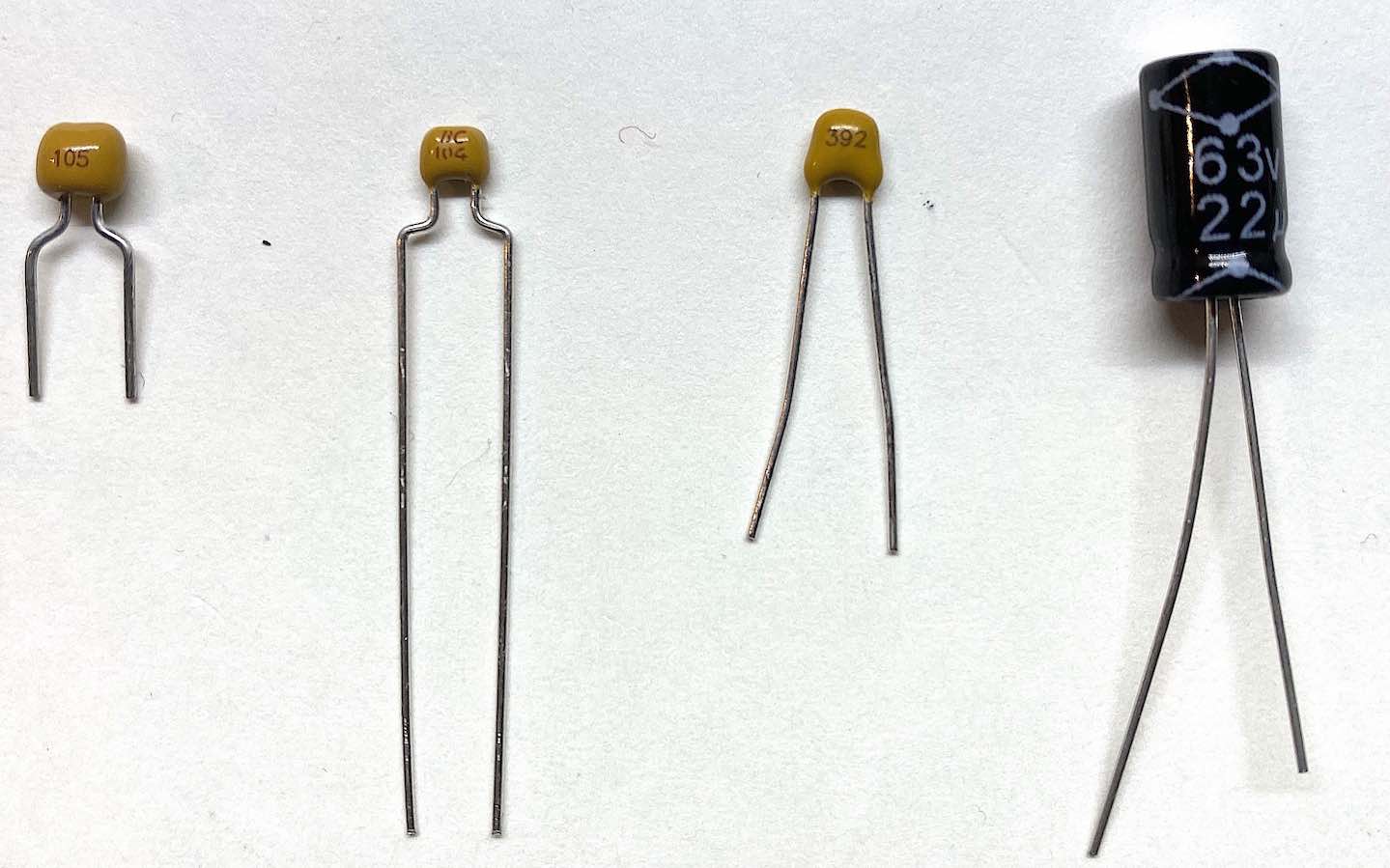
3 Ceramic disc capacitors and and 22uF electrolytic capacitor
- on the left is a 1uF (\(\mathrm{\equiv 1 \mu F}\)) capacitor, identified by its 105 capacitor code which is read as \(10\times10^5\) pF.
- the “BC” on the second 0.1uF capacitor is just the manufacturer’s logo.
- the third ceramic capacitor’s value is \(\mathrm{39\times 10^2\,pF = 3.9\,nF}\)
- See how to read a ceramic capcitor code
- Note that electrolytic capacitors are polarized, i.e. the long leg should at a higher (i.e. more positive) potential than the shorter leg.
Inductors
- Note that large inductors have relatively low maximum currents, e.g. as little as 3V DC could fry a 47mH inductor with \(162\Omega\) internal resistance and maximum DC current of 16mA.