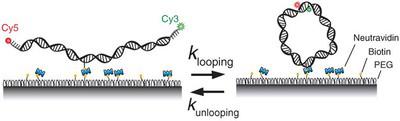
The classical view of DNA posits that DNA must be stiff below the persistence length [<150 base pairs (bp)], but recent studies addressing this have yielded contradictory results. We developed a fluorescence-based, protein-free assay for studying the cyclization of single DNA molecules in real time. The assay samples the equilibrium population of a sharply bent, transient species that is entirely suppressed in single-molecule mechanical measurements and is biologically more relevant than the annealed species sampled in the traditional ligase-based assay. The looping rate has a weak length dependence between 67 and 106 bp that cannot be described by the worm-like chain model. Many biologically important protein-DNA interactions that involve looping and bending of DNA below 100 bp likely use this intrinsic bendability of DNA. I will also present a more recent study where we use DNA as a tension gauge tether to define the single molecule forces required to activate cellular signaling through membrane receptors.
-
- Illustration: Ha

